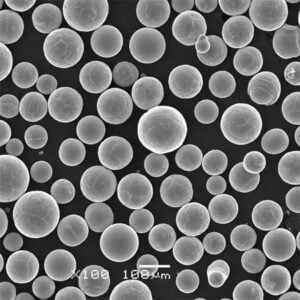
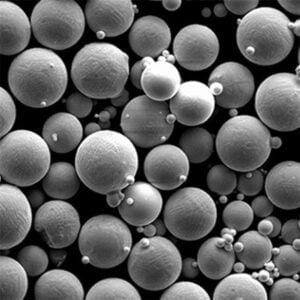
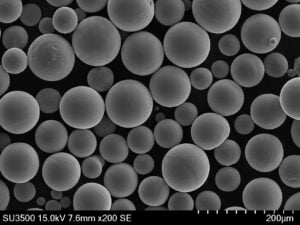
Titannitrid (TiN)-Pulver ist ein extrem hartes keramisches Material mit einzigartigen Eigenschaften, die es für den Einsatz in verschiedenen Branchen geeignet machen. Dieser Artikel bietet einen Überblick über Titannitrid-Pulvereinschließlich der Zusammensetzung, der wichtigsten Merkmale, des Herstellungsprozesses und der Anwendungen.
Überblick über Titannitrid-Pulver
Titannitrid oder TiN ist eine goldgelbe Keramikverbindung, die aus Titan- und Stickstoffatomen besteht. Seine chemische Formel lautet TiN.
Zu den wichtigsten Merkmalen von Titannitridpulver gehören:
- Extreme Härte - fast so hart wie Diamant
- Ausgezeichnete Verschleiß- und Korrosionsbeständigkeit
- Hohe thermische Stabilität
- Metallische Goldfarbe
- Elektrisch leitfähig
- Biokompatibel und ungiftig
Seine einzigartige Kombination von Eigenschaften hat dazu geführt, dass TiN-Pulver unter anderem für Oberflächenbeschichtungen von Werkzeugen, Automobilkomponenten, Turbinen und medizinischen Implantaten verwendet wird.
In den folgenden Abschnitten werden die Zusammensetzung, die Eigenschaften, die Herstellung und die Verwendung von Titannitridpulver näher erläutert.

Zusammensetzung und Merkmale von Titannitrid-Pulver
| Eigentum | Beschreibung | Einheiten |
|---|---|---|
| Chemische Formel | TiN | |
| Chemische Zusammensetzung (typisch) | – Titanium (Ti): Min. 77.0 wt%<br> – Nitrogen (N): Min. 20.0 wt%<br> – Carbon (C): Max. 0.1 wt% | wt% |
| Kristallstruktur | NaCl-type face-centered cubic | |
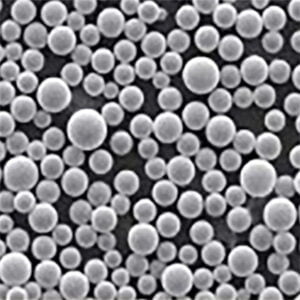
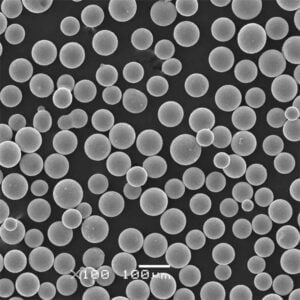
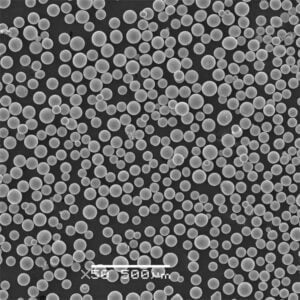
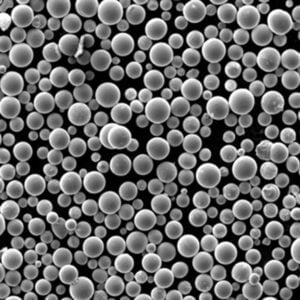
| Partikelgröße | Variiert je nach Anwendung<br> – Micronized powders: < 10 microns<br> – Submicron powders: < 1 micron<br> – Nanopowders: < 100 nanometers | microns, nanometers |
| Erscheinungsbild | Gold-colored | |
| Schmelzpunkt | ~2930°C | °C |
| Dichte | 5.22 – 5.44 g/cm³ | g/cm³ |
| Härte | Vickers hardness: 1800-2100 HV<br> Mohs hardness: 8-9 | HV |
| Elastizitätsmodul | 550 ± 50 GPa | GPa |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient | 9.35 × 10⁻⁶ K⁻¹ | K⁻¹ |
| Elektrische Leitfähigkeit | Metallic conductor (conductivity varies with stoichiometry and impurities) | S/m |
| Wärmeleitfähigkeit | High (15-30 W/mK) | W/mK |
| Superconducting Transition Temperature | Up to 6.0 K (single crystals) | K |
| Chemische Beständigkeit | Excellent resistance to most chemicals at room temperature<br> Reacts with oxygen at high temperatures (> 800°C) | |
| Biokompatibilität | Generally considered biocompatible |
Herstellungsverfahren für Titannitrid-Pulver
| Prozess | Beschreibung | Vorteile | Benachteiligungen |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nitridation | This is the most widely used method for producing titanium nitride powder. It involves reacting titanium feedstock with nitrogen gas or ammonia at high temperatures (typically above 900°C). The reaction can be carried out in various reactor configurations, including fluidized beds, rotating reactors, and plasma reactors. | – Established and reliable technology – Produces high-purity TiN powder – Offers good control over powder morphology | – Requires high temperatures, leading to increased energy consumption – Particle size and size distribution can be difficult to control at high temperatures – Potential for oxygen contamination if not carefully controlled |
| Carbothermal Reduction | This method involves heating a mixture of titanium dioxide (TiO2), carbon (graphite or charcoal), and nitrogen gas to high temperatures (around 1300°C). The carbon acts as a reducing agent, converting the titanium dioxide to titanium nitride. | – Offers a potentially lower cost alternative to nitridation – Can be used to produce titanium nitride with specific carbonitride compositions | – More complex reaction chemistry compared to nitridation – Strict control over the starting material ratio and reaction conditions is crucial to achieve desired product purity – May require additional post-processing steps to remove impurities |
| Reactive Ball Milling | This is a high-energy mechanochemical process where titanium powder and a nitrogen source (often urea) are milled together in a high-energy ball mill. The mechanical force from the milling balls fractures the particles and promotes the solid-state reaction between titanium and nitrogen, forming titanium nitride at relatively low temperatures (around room temperature). | – Suitable for producing nano-sized titanium nitride powder – Lower energy consumption compared to high-temperature methods – Can be a scalable process | – Relatively new technology with ongoing research and development – May introduce contamination from the milling media – Achieving uniform particle size distribution can be challenging |
| Chemische Gasphasenabscheidung (CVD) | This method involves introducing precursor gases containing titanium and nitrogen into a heated reaction chamber. The precursor gases decompose and react to form titanium nitride particles, which are then deposited on a substrate or collected as powder. | – Highly versatile method capable of producing powders with tailored properties – Enables precise control over particle size and morphology | – Complex and expensive process equipment required – Limited production capacity compared to other methods – Safety considerations due to the use of potentially hazardous precursor gases |
| Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) | Similar to CVD, PVD involves vaporizing titanium in a vacuum environment and reacting it with nitrogen gas. The vaporized titanium can be generated using various techniques such as sputtering, cathodic arc deposition, or electron beam evaporation. | – Suitable for producing high-purity and well-defined titanium nitride thin films or powders – Offers good control over film thickness and composition | – Highly specialized and expensive equipment – Limited production rate for powder production – Line-of-sight deposition, making it unsuitable for complex geometries |
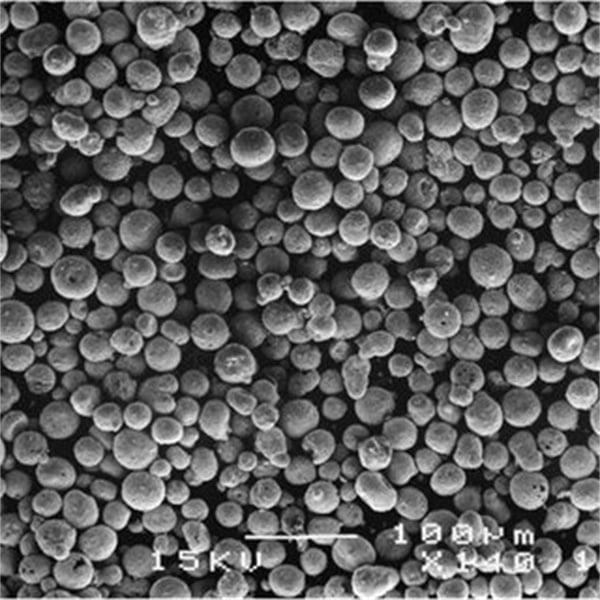
Anwendungen und Verwendungen von Titannitrid-Pulver
| Kategorie | Anmeldung | Immobilien gehebelt | Einzelheiten |
|---|---|---|---|
| Schneidewerkzeuge | Drill bits, milling cutters, end mills | High hardness, wear resistance, low friction coefficient | Titanium nitride (TiN) powder is a popular choice for coating cutting tools due to its exceptional hardness, which extends tool life by up to three times compared to uncoated tools. The low friction coefficient of TiN coatings reduces friction between the tool and workpiece, minimizing heat generation and improving cutting efficiency. Additionally, TiN’s wear resistance prevents chipping and degradation of the cutting edge, maintaining sharp cuts for longer. |
| Medizinische Geräte | Scalpel blades, bone saws, orthopedic implants | Biocompatibility, wear resistance, sharpness | In the medical field, TiN powder finds application in coating surgical instruments like scalpels and bone saws. Its biocompatible nature makes it safe for implantation within the body. Furthermore, the wear resistance of TiN coatings ensures that these instruments retain their sharpness during procedures, leading to cleaner cuts and improved patient outcomes. TiN is also used to coat some orthopedic implants, such as hip replacements, due to its ability to enhance wear resistance and reduce friction at the implant-bone interface, promoting long-term implant stability. |
| Decorative Coatings | Costume jewelry, automotive trim | Attractive golden color, high durability | Beyond its functional applications, TiN powder is valued for its aesthetic properties. The metallic gold color of TiN coatings makes them ideal for decorative purposes in costume jewelry and automotive trim. Unlike real gold plating, TiN offers superior durability and scratch resistance, maintaining its shine for extended periods. This combination of aesthetics and functionality makes TiN powder an attractive choice for manufacturers seeking a balance between style and longevity. |
| Konsumgüter | Plumbing fixtures, doorknobs | Corrosion resistance, wear resistance, aesthetic appeal | The beneficial properties of TiN extend to everyday consumer goods. A common application is in the coating of plumbing fixtures and doorknobs. The corrosion resistance of TiN protects these items from tarnishing and wear, particularly in areas exposed to moisture. Additionally, the wear resistance of TiN coatings prevents scratches and maintains the smooth operation of faucets and door handles. In some cases, a top layer of TiN is used over a nickel or chromium base coat, providing a combination of durability, corrosion resistance, and a touch of golden elegance. |
| Semiconductors | Diffusion barriers, electrical conductors | High thermal stability, good electrical conductivity | Within the realm of semiconductors, TiN powder plays a crucial role in the fabrication process. Thin films of TiN are deposited onto silicon wafers to act as diffusion barriers, preventing unwanted elements from migrating through the layers and disrupting the electrical properties of the device. TiN also exhibits good electrical conductivity, making it suitable for use as electrical contacts within integrated circuits. |
| Aufkommende Anwendungen | Solar cells, architectural coatings | Broad spectrum of properties | Research and development efforts are exploring new applications for TiN powder. In the field of solar energy, TiN coatings are being investigated for their potential to improve the efficiency of solar cells. The ability of TiN to absorb certain wavelengths of light while reflecting others could lead to the development of more efficient light-harvesting devices. Additionally, TiN’s combination of properties, including hardness, corrosion resistance, and a self-lubricating effect, makes it a promising candidate for architectural coatings on buildings. These coatings could offer protection against harsh weather conditions, improve self-cleaning properties, and potentially enhance the aesthetic appeal of structures. |
Spezifikationen von Titannitrid-Pulver
Titaniumnitridpulverprodukte sind in verschiedenen Reinheitsgraden, Partikelgrößenverteilungen und Morphologien erhältlich und können je nach Anwendungsanforderungen angepasst werden.
Einige wichtige Spezifikationen für TiN-Pulver:
| Spezifikation | Einzelheiten |
|---|---|
| Reinheit | 99% Titannitrid-Mindestgehalt für die meisten Anwendungen. Auch niedrigere Reinheiten ~92%-95% für unkritische Anwendungen. |
| Morphologie der Partikelform | Variiert von kugelförmig, agglomeriert bis kantig |
| Verteilung der Partikelgröße (d50) | Die Bandbreite reicht von 30-50 nm im Nanobereich bis zu 2-5 μm im Mikrometerbereich für Beschichtungen von Werkzeugen/Komponenten. Submikronqualität ~0,5 μm ebenfalls üblich. |
| Spezifische Oberfläche (SSA) | Von niedrigen 5 m2/g für Mikronqualitäten bis 15-30 m2/g für Nanopulver |
| Farbe | Metallisches Hellgold |
| Schmelzpunkt | 2950°C |
| Mohshärte | 8.5 |
| Kristallstruktur | Kubisch - Typ NaCl |
| Dichte | 5,22 g/cm3 |
| Sauerstoff-/Kohlenstoffgehalt | Unter 1% ist der Sauerstoffgehalt wichtig für hohe Reinheit |
Tabelle 1: Zusammenfassung der Spezifikationen von Titannitrid
Diese Pulverspezifikationen können bei der kundenspezifischen Herstellung je nach den Anwendungen der Zielbranche variiert werden.
Globale Anbieter und Preisgestaltung
| Region | Major Suppliers | Produkt | Preis (USD/kg) | Wichtige Überlegungen |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nordamerika | American Elements, US Titanium Mills, Nanoventure | Micronized TiN (>1 micron) | 100-200 | Offers good balance between cost and performance for wear-resistant coatings |
| Alfa Aesar, ATI Specialty Materials | Nanometerized TiN (<100 nm) | 400-800 | High surface area ideal for electronics and catalysis applications | |
| Praxair Oberflächentechnologien | Feedstock for CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) | Price upon request | Consistent quality and particle size crucial for thin film coatings | |
| Europa | H.C. Starck, Sandvik Hyperion, Plansee | General purpose TiN | 80-150 | Wide availability from reputable European producers |
| Evonik Industries, Arkema | High purity TiN (99.9%+) | 250-500 | Demanded by aerospace and medical device industries | |
| NanoMaterials | Ultrafine TiN (<50 nm) | 800-1200 | Leading supplier for research and development purposes | |
| Asien-Pazifik | China National Bluestar (CNB), Fangda Carbon New Material, Ningbo Tianxiang | Commercial grade TiN | 50-80 | Cost-effective option for bulk applications |
| Toda Metal, Mitsui Mining & Smelting | High performance TiN | 120-200 | Known for quality and consistency in Asia | |
| Kojundo Chemical Laboratory | Specialized TiN grades (e.g., doped) | Price upon request | Expertise in custom-engineered powders for specific needs |
Vergleich zwischen Titannitrid und anderen harten Beschichtungen
Eigenschaften im Vergleich
| Eigenschaften | Titannitrid | Chromnitrid | Aluminium-Titannitrid | Diamantähnlicher Kohlenstoff | Titankarbid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Härte (HV) | 2000 – 2400 | 1400 – 1800 | 3200 – 3400 | 1000 – 1500 | 2800 – 3400 |
| Stärke | Ausgezeichnet | Gut | Überlegene | Sehr gut | Extrem hoch |
| Abnutzungswiderstand | Extrem hoch | Mäßig | Außergewöhnlich hoch | Mäßig | Außergewöhnlich hoch |
| Korrosionsbeständigkeit | Hoch | Mäßig | Sehr hoch | Niedrig | Hoch |
| Oxidationsbeständigkeit | Mäßig | Gut | Ausgezeichnet | Gut | Gut |
| Reibungskoeffizient | 0.5 | 0.35 – 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.1 – 0.2 | 0.25 – 0.35 |
| Farbe | Helles Gold | Gray | Dunkelviolett | Graphitgrau | Blaugrau |
| Max. Betriebstemp. (°C) | 500 | 750 | 800 | 250 | 600 |
| Kosten | Mäßig | Niedrig | Hoch | Hoch | Hoch |
| Toxizität | Ungiftig | Enthält Cr, Co | Ungiftig | Ungiftig | Ungiftig |
Vorteile von Titannitrid
Einige Vorteile und Vorzüge von Titannitridbeschichtungen gegenüber anderen Alternativen:
- Extreme Härte für den Verschleißschutz mit einer Bewertung vergleichbar mit TiC
- Korrosionsbeständigkeit für die meisten Produktionsumgebungen geeignet
- Hohe Temperaturstabilität bei einer Härte von bis zu 500°C
- Geringe Toxizität - im Gegensatz zu CrN sicher für medizinische Geräte/Implantate
- Ausgezeichnete Haftung auf Titanlegierungen und Edelstahlsubstraten
- Bio-inert erleichtert die Zulassung der Biokompatibilität
- Neutraler Reibungskoeffizient verhindert das Festfressen von Teilen
- Höhere Oxidationsbeständigkeit gegenüber TiC-Beschichtungen
Beschränkungen von Titannitrid
Obwohl Titan-Nitrid eine sehr vielseitige Leistung aufweist, gibt es einige Einschränkungen:
- Geringere Temperaturstabilität als AlTiN, das über 800°C stabil ist
- Relativ geringere Zähigkeit und Stoßfestigkeit als DLC
- Höhere Spannungen in der Beschichtung können mit der Zeit zu Rissen/Ablagerungen führen.
- Nicht für saure Umgebungen empfohlen, da spontane Oxidation
- Teurer im Vergleich zu einfachen Cr- oder WC-Beschichtungen
- Metallbearbeitungsprozesse können metallische Ablagerungen über die TiN-Beschichtung schmieren
Wann sollte man sich für Alternativen zu Titannitrid entscheiden?
Andere Beschichtungen können besser geeignet sein als TiN, wenn:
- Betriebstemperaturen über 500°C (AlTiN oder Chromnitrid verwenden)
- Hervorragende Zähigkeit gegen Stoßbelastungen erforderlich (DLC berücksichtigen)
- Durchleitung von RF-Signalen erforderlich, z. B. Luft- und Raumfahrt/Telekommunikation (DLC bessere Option)
- Exposition gegenüber Halogensäuren oder anderen stark korrosiven Medien (DLC wählen)

Vor- und Nachteile der Titaniumnitrid-Beschichtung
| Merkmal | Profis | Nachteile |
|---|---|---|
| Abnutzungswiderstand | * Significantly extends tool life by reducing friction and wear. Cutting tools, drill bits, and other implements last longer, reducing replacement costs and downtime. * Offers superior protection against abrasive materials, making it ideal for machining composites, wood, and certain metals. | * Brittleness: While hard, TiN can chip or flake if subjected to high impact or excessive force. May not be suitable for heavy-duty percussion applications. * Thickness |
| Friction Reduction | * Lowers friction coefficient, leading to smoother cutting operations. This reduces heat generation, which can damage tools and degrade workpiece quality. * Minimizes energy consumption during machining, resulting in cost savings and a more environmentally friendly process. | * Performance may vary depending on the material being machined. Lubrication might still be necessary for some applications. |
| Korrosionsbeständigkeit | * TiN acts as a barrier against corrosion, protecting the underlying metal from rust and other environmental factors. * Maintains the integrity and functionality of tools and components in harsh environments. | * Not as effective against certain chemicals or highly corrosive substances. * Other coatings might be better suited for extreme corrosion resistance needs. |
| Thermische Stabilität | * Performs well at elevated temperatures, making it suitable for high-speed machining applications. * Reduces heat-related tool wear and maintains dimensional accuracy of machined parts. | * May not be the best choice for extremely high-temperature environments where other advanced coatings excel. |
| Aesthetics | * Distinctive golden or yellowish hue often associated with high-performance tools. * Enhances the visual appeal of certain products. | * Cosmetic benefit is secondary to the functional advantages. * Color can vary slightly depending on the deposition process. |
| Kosten | * Relatively affordable compared to some other advanced coating technologies. * Provides significant performance improvement at a reasonable cost point. | * Initial coating cost needs to be weighed against the benefits of extended tool life and improved machining efficiency. |
| Auswirkungen auf die Umwelt | * Reduces waste by extending tool lifespan, requiring fewer replacements. * Contributes to a more sustainable machining process. | * The coating process itself might involve the use of specific chemicals, requiring proper disposal procedures. |
FAQ
F: Warum hat Titannitrid eine goldene Farbe?
A: Die goldene Farbe resultiert aus den Lichtabsorptions-/Reflektionseigenschaften der kristallinen Struktur von Titannitrid, die plasma- oder dampfförmig abgeschiedenen TiN-Beschichtungen ihre charakteristische goldene Oberfläche verleiht.
F: Ist Titannitrid giftig?
A: Nein, Titannitrid-Keramik gilt als völlig ungiftig und bioinert, so dass sie gemäß der Biokompatibilitätsnorm ISO 10993 sicher für die Verwendung in biomedizinischen Implantaten ist.
F: Welche Dicke der TiN-Beschichtung sollte verwendet werden?
A: Der typische Schichtdickenbereich liegt bei 1-5 Mikron. Dünnere Schichten von 0,5-1 Mikron bieten Verschleißschutz. Schichten von 2-5 Mikron bieten Korrosions- und Erosionsbeständigkeit für eine längere Lebensdauer.
F: Erhöht oder verringert die TiN-Beschichtung die Reibung?
A: TiN verringert den Reibungskoeffizienten gegenüber Stahl erheblich. Die genauen Werte liegen zwischen 0,4 und 0,9, je nach Gegenstückmaterial, wodurch die Gesamtreibung verringert, aber ein Festfressen verhindert wird.
F: Wie hoch ist die typische Härte von Titannitridschichten?
A: Die Härtewerte liegen zwischen 2000 und 2500 Vickers, wenn sie als dünne Schichten mittels PVD- oder CVD-Verfahren abgeschieden werden, was zu den höchsten Werten gehört, die für kommerzielle Beschichtungen erreichbar sind.
F: Was ist Aqua-Titannitrid?
A: Aqua TiN bezieht sich auf eine Titancarbonitrid-Beschichtung, die mit 8-20%-Silizium legiert ist und eine aquablaue Farbe sowie hervorragende tribologische Eigenschaften bis zu 700 Grad Celsius aufweist. C Temperaturen.
F: Verhindert die TiN-Beschichtung Abrieb und Adhäsionsverschleiß?
A: Ja, Titannitrid wird häufig in Anwendungen wie Umformung/Stanzen/Ziehen eingesetzt, wo es als hervorragende Anti-Galling- und Anti-Fresser-Beschichtung dient, selbst unter Grenzschmierbedingungen.
F: In welchen Branchen werden Titannitridbeschichtungen verwendet?
A: Alle wichtigen Produktionssektoren, einschließlich der Automobil-, Luft- und Raumfahrt-, Textil-, Verpackungs-, Elektronik-, Stahl-, Petrochemie- und Medizinbranche usw. verwenden TiN-Schichten, um die Leistung und Zuverlässigkeit von kritischen Teilen und Werkzeugen zu verbessern.